merge into 调研笔记
a.k.a. Upsert, SQL:2003 标准引入,能够在一条 sql 语句中,根据不同的条件,分别执行 update、delete 和 insert,非常强大好用。
有许多数据库都实现了 merge 的功能,包括 PostgreSQL, DB2 等,也有一些数据库实现了类似的功能,如 MySQL 的 insert .. on duplicate key, replace 等。
本文主要研究 Oracle 12 中 merge 的实现,并给出在 KunDB 中实现 merge 的一些想法。
Introduction
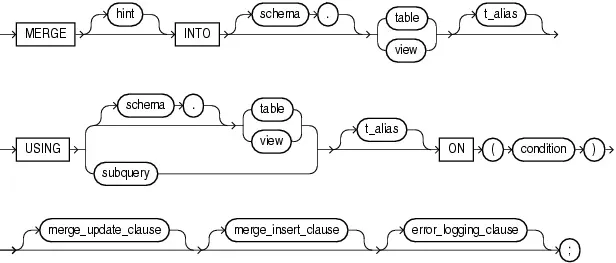
merge 语法
merge into 主要分为三个主要分支:主分主,update 分支和 insert 分支:
- 主分支:通过 into 子句指定了 merge 的 TARGET,即 merge 操作的目标表,无论后续执行 update 还是 insert,抑或是 delete,都是在 target 上执行的;通过 using 子句指定了 merge 的 SOURCE,即 merge 操作的源,源指定了数据的来源,可以是表,视图或者子查询。merge 可以使用 source 返回的数据来更新或者将其插入到 target 中;on 子句指定了匹配条件,后续执行的具体操作由 on 子句指明,如果 on 中表达式返回 true,即匹配,则执行 update 分支,如果返回 false 或者 null,则不匹配,执行 insert 分支。
-
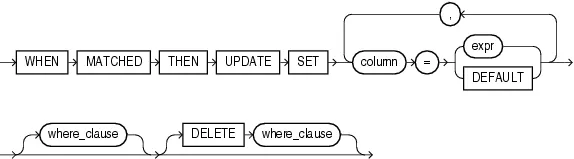
update 分支:当 on 子句中指定的条件返回 true 时,会执行 update 分支,会根据 set 子句指定的表达式对 target 表进行更新,也可以指定 where 子句,这样只会对 target 中满足 where 条件的行进行更新。
不能 update 在 on 条件中出现的列。
在 update 分支中可以指定 delete 操作:
-
delete 不会删除 insert 插入的数据
The only rows affected by this clause are those rows in the destination table that are updated by the merge operation.
-
delete 的 where 条件是根据 update 之后的数据进行评估的
The
DELETEWHEREcondition evaluates the updated value, not the original value that was evaluated by theUPDATESET…WHEREcondition. -
源表中没有被 join 选取的行,即使满足 delete 条件,也不会被删除
If a row of the destination table meets the
DELETEcondition but is not included in the join defined by theONclause, then it is not deleted.
-
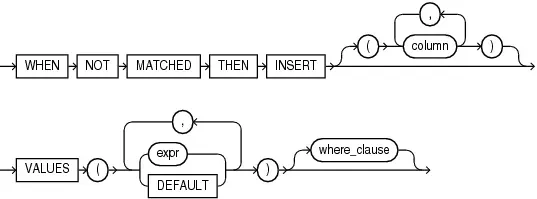
- insert 分支:当 on 子句返回 false 时,执行 insert 分支。如果 on 子句的条件是 constant filter predicate,如
ON(0=1),Oracle 会将 merge 转为 insert,避免 join。同样,insert 也可以指定 where 子句,当满足条件时才会插入。-
insert 可能会导致主键冲突
-- t1: (1,2),t2: (1,3) && t1.a is primary key merge into t1 using t2 on (t1.b = t2.b) when not matched then insert values(t2.a, t2.b); -
merge 的 delete 和 update 对 insert 可见
-- t1: (1,2), t2: (1,3),(2,2) && t1.a is primary key merge into t1 using t2 on (t1.b = t2.b) when matched then update set a = t2.a [delete where a = 2] when not matched then insert values(t2.a, t2.b);
-
其他需要注意的地方:
-
merge是一个确定性的陈述,无法在同一 merge 语句中多次更新目标表的同一行
需要 Single Join,或者 merge 算子进行 runtime 检测
merge 执行
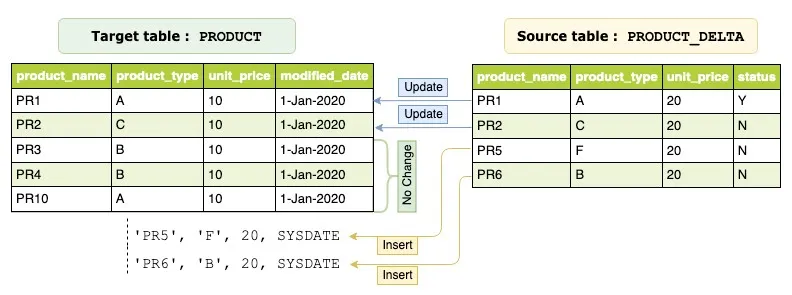
MERGE INTO PRODUCT prd
USING PRODUCT_DELTA src
ON (prd.product_name = src.product_name
AND prd.product_type = src.product_type
)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
prd.unit_price = src.unit_price,
modified_date = SYSDATE
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT(product_name, product_type, unit_price, modified_date)
VALUES(src.product_name, src.product_type, src.unit_price, SYSDATE);
merge 首先会 perform 一个 left join,即 source RIGHT OUTER JOIN target ON match_condtion,并以 left join 的数据为输入,进入 merge 的处理流程。
朴素算法:
for each row in INPUT
a <- matched(row) // 对于输入的每一行,判断是否匹配
if a is true // 匹配上了,走 update 分支
b <- calc_where(update_where, row) // 判断 update 的 where 条件是否为真
if b is true // 满足 update 的条件
new_row <- calc_update(row) // 根据 set 子句,计算出 new_row
c <- calc_where(delete_where, new_row) // 用更新后的数据计算 delete 的 where 条件是否为真
if c is true // 满足 delete 的条件
delete_target(row) // 从 target 中删除该行
else // 不满足 delete 的条件
update_target(row, new_row) // 更新 target
endif
endif
else // 没有匹配上,走 insert 分支
d <- calc_where(insert_where, row) // 判断 insert 的 where 条件是否为真
if d is true
insert_target(row) // 将 source 的数据插入到 target 中
endif
endfor